Related News
Related News
-
EWEB Board of Commissioners selects BPA administrator for general manager role
In a unanimous vote, EWEB’s Board voted to move forward with negotiating an employment offer to BPA’s John Hairston.
Find Out More -
EWEB and Lane Electric Cooperative sign agreement to transfer EWEB's McKenzie Valley customers
EWEB and Lane Electric Cooperative have reached an important milestone in transitioning electric service from EWEB to Lane Electric in the McKenzie Valley. The two utilities have officially signed agreements for EWEB to sell its electric service territory in the McKenzie Valley to Lane Electric.
Find Out More -
EWEB Board adopts 2026 organizational goals to guide utility priorities
At the January public meeting, EWEB adopted a new set of organizational goals for 2026, providing direction for our work priorities in the year ahead.
Find Out More -
Cold temperatures this week drive highest electricity demand of the winter so far
Frosty conditions in Eugene this week have driven electricity demand to the highest levels so far this winter as heaters strain to keep homes and businesses warm.
Find Out More -
Our Favorite Photos of 2025
For a final look-back at 2025, we’d like to share some of our favorite photos that illustrate our work day-in and day-out. We celebrate amazing teamwork, vital partnerships, and sing the praises of our individual champions and their quiet dedication to serving our community!
Find Out More -
EWEB and the UO launch energy generation pilot project
Pilot project gives EWEB the option to run UO’s on-site natural gas generator this winter, gathering valuable insight into the generator’s efficiency and reliability.
Find Out More -
EWEB secures $2.5 billion of reliable, affordable, carbon-free energy for customers
The new contract with EWEB’s largest energy supplier, the Bonneville Power Administration, forms the foundation of a diverse energy portfolio.
Find Out More -
Women in STEM: Meet the Hydro Project Engineer Building Habitat for Salmon
EWEB Engineer Associate Val Chang found her way to the McKenzie River from Los Angeles, inspired by heritage trips to the waters of Taiwan and key mentors along the way.
Find Out More -
Public Power Week Poster Contest Winners 2025
The results are in! View the winning posters from EWEB's 2025 Public Power Week Poster Contest.
Find Out More -
EWEB Hometown Heroes compete internationally
Out of 290 teams from 14 different countries, EWEB's Lineman Rodeo team places in the top third of competitors.
Find Out More -
Vote for your favorite Public Power Week Posters
The top five submittals will receive awards. Help us pick the winners.
Find Out More -
Electric Projects underway in North & South Eugene
Underground lines and disaster-resilient power poles are part of EWEB’s infrastructure upgrade near Eugene’s largest natural resource area.
Find Out More -
The Bonneville Power Administration Rate Change and Your EWEB Bill
BPA’s finalized rate increase is smaller than projected, and EWEB’s pass-through adjustment effective October 1, 2025 will now be 2.7% for residential customers—down from the anticipated 4%.
Find Out More -
EWEB completes helicopter installation of salmon habitat features
EWEB adds downed trees and 2,000 tons of gravel to the Uupper McKenzie River below Tamolitch Falls to improve spawning habitat.
Find Out More -
Court rules in favor of EWEB in Carmen-Smith litigation
The U.S. District Court in Eugene has granted EWEB's motion to dismiss a lawsuit brought under the Endangered Species Act pertaining to fish passage at EWEB’s Trail Bridge Dam. The favorable ruling clears the way for EWEB to continue advancing towards implementation of permanent fish passage at the dam.
Find Out More - Show More
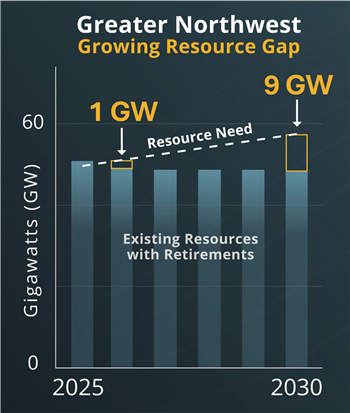
Energy shortfall of 9 gigawatts projected for the Northwest
December 18, 2025 • Aaron Orlowski, EWEB Communications
If a severe cold snap strikes the Northwest during a dry year, energy shortages could lead to rolling blackouts, according to the initial results of a study published by the consulting firm Energy and Environmental Economics.
Download a fact sheet about the study.
The study was commissioned by the Public Generating Pool (PGP), a trade organization of which the Eugene Water & Electric Board (EWEB) is a member, as well as more than a dozen other Northwest utilities and power producers.
The risk is imminent. If a dry year constrains the region’s hydropower resources and an extended cold snap causes energy demand to soar, the shortfall in the Greater Northwest — a region encompassing Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming and parts of a few other states — could reach 1 gigawatt in 2026.
By 2030, the shortfall in the Greater Northwest could soar to 9 gigawatts, or roughly the electricity demand of the entire state of Oregon. In just Oregon and Washington, the projected shortfall is 5 gigawatts by 2030.
Under these conditions, a shortage could last for several days.
“There is only one way for us to prepare for and overcome this challenge, and that’s by working in partnership,” said EWEB Chief Energy Resources Officer Brian Booth, who is also the volunteer treasurer of PGP. “During those rare moments when the power system treads close to the edge of crisis, we will lean on each other. We’ll need to turn on the last-resort power plants. We’ll need to lean on partnerships with large customers to manage supply and demand. And we’ll need residential customers across the board to pare back where they can until the crisis passes.”
Rising electricity demand and an insufficient buildout of new generation has led to the gap.
Electricity demand in the Northwest is forecasted to rise 30% in the next decade, according to the 2025 Pacific Northwest Utilities Coordinating Council (PNUCC) Regional Forecast. Demand for electricity is rising as people swap their gasoline-powered cars for electric vehicles and switch their gas furnaces for electric heat pumps. But the largest driver of rapid, near-term increases in electricity demand is the growth of data centers.
As demand rises, the region has failed to build enough new power plants to keep up, creating a widening gap between electricity supply and demand. The resources that utilities across the region have built in recent years are mainly weather-dependent renewables such as wind and solar — resources can’t be counted on during extended cold snaps.
The challenge in the Northwest differs from neighboring regions. California, for instance, typically faces peaking electricity demand in the early evening hours of hot summer days, when air conditioning use soars. That demand coincides with when the sun is setting and solar generation is fading. An effective solution has been to build batteries to store abundant afternoon solar power for a few hours into the evening before temperatures cool off. With over 10 gigawatts of new battery storage built in just the last couple of years, California has largely solved their resource adequacy issues that arose in recent years.
But in the Northwest, multi-day cold snaps occur when clouds cover the sky and wind often comes to a standstill, causing renewable generation to bottom out. Wind, solar and batteries simply can’t supply enough energy to meet demand at those times. The study showed that while 4-hour batteries were a right-sized solution for California’s evening peaks, they are not cost-effective at solving the Northwest’s 100-hour cold events.
“Electrification is key to reducing carbon emissions. Any time we can replace fossil fuel use with clean electricity, that’s a good decision,” Booth said. “But we need to electrify in a smart way. That means ensuring our electric usage is flexible so that when electricity demand soars, we can pare back electricity usage temporarily. Usually, that will be a few hours. On rare occasions, such as these extended cold snaps, it will be a few days.”
Read regional media coverage of the study:
Related Programs
EWEB’s energy supply planning process examines possible energy resource portfolios with a goal of creating useful insights for long-term (20-year) electricity supply planning decisions.




